Follow-Up Actions
After the agent provides information to the user, we can add follow-up actions to enrich the interaction between the agent and the user, rather than always requiring the user to interact via text.
Follow-up actions can be divided into three types:
- Recommended Follow-Up Questions: After answering, the agent can suggest some follow-up questions that the user can click on directly to ask.
- Follow-Up Actions: After answering, the agent can display action buttons for the user to click, such as "Next Step," "Cancel Operation," etc.
- Follow-Up Options: The agent can display a series of options for the user to select, which can be single-choice or multiple-choice.
Recommended Follow-Up Questions
Recommended follow-up questions are returned to the client in the following XML format:
<followup>
<questions>
<question>
</question>
</questions>
</followup>You can instruct the LLM to return this XML format in the prompt, for example:
You are an AI customer service agent tasked with assisting users.
First, answer the user's question, and then, based on the user's question and your response, recommend some follow-up questions in the user's tone.
Use the following format to return the follow-up questions:
<followup>
<questions>
<question>
</question>
</questions>
</followup>The client will display the recommended follow-up questions based on the returned XML format, as shown in the image below:
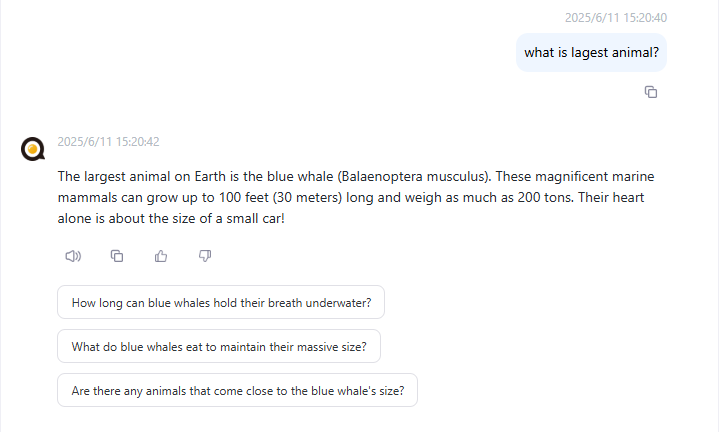
When the user clicks on a question, the following JSON object will be sent to the server:
{
"question": "Question content"
}When the agent receives this response, it does not need to process it further and can directly submit this string to the LLM for answering.
Follow-Up Actions
Follow-up actions are returned to the client in the following XML format:
<followup>
<actions>
<action>
<label>Button name</label>
<value>Value returned when the button is clicked</value>
</action>
</actions>
</followup>Depending on your agent's logic, you can use an output node to return fixed follow-up action XML content or let the LLM generate the follow-up action XML content.
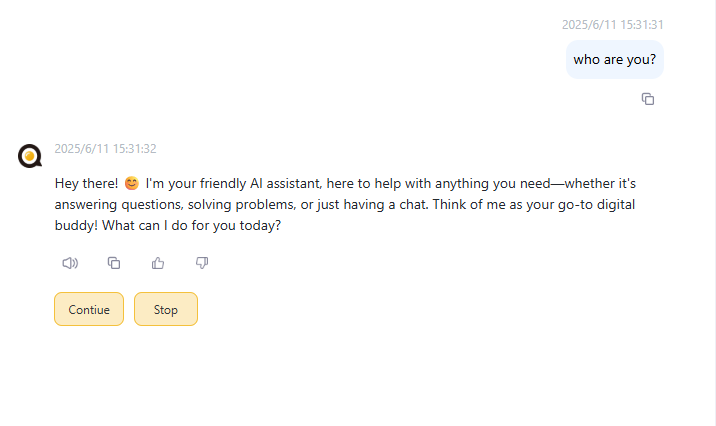
When the user clicks a button, the following JSON object will be sent to the server:
{
"action": "Value returned when the button is clicked"
}The agent can use a Compute node or a Boolean function-type Judge node to handle this response:
const str = `{{sys.userMessage}}`;
const response = JSON.parse(str);
console.log(response.action);Follow-Up Options
Follow-up options are returned to the client in the following XML format:
<followup>
<options multiple="true">
<option>
<label>Option name</label>
<value>Value returned when the option is clicked</value>
</option>
</options>
</followup>Depending on your agent's logic, you can use an output node to return fixed follow-up option XML content or let the LLM generate the follow-up option XML content.
For example, you can use this prompt to instruct the LLM to generate follow-up option XML content:
You are a restaurant's AI customer service agent tasked with taking orders for users.
Based on the restaurant's menu, recommend some dishes to the user.
Use the following format to return the follow-up options:
<followup>
<options multiple="true">
<option>
<label>Option name</label>
<value>Value returned when the option is clicked</value>
</option>
</options>
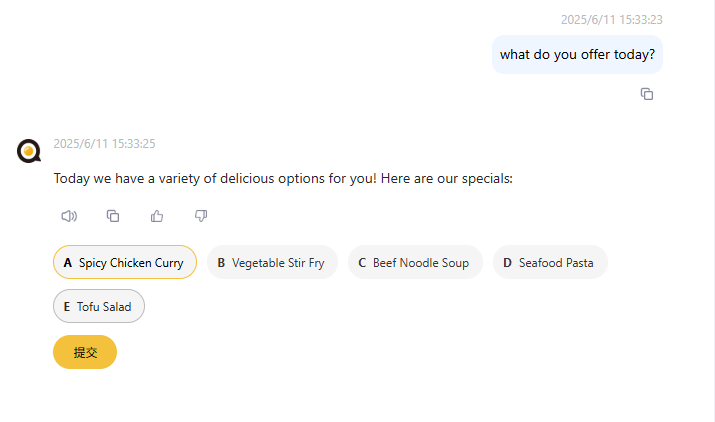
</followup>When the user clicks on an option, the following JSON object will be sent to the server:
{
"options": ["Option value 1", "Option value 2", "Option value 3"]
}
The agent can subsequently use a Compute node to handle this response. For example:
const str = `{{sys.userMessage}}`;
const response = JSON.parse(str);
console.log(response.options);